Being a type of auxiliary verb, the modal verb is mainly used when speakers tend to express moods or attitudes (Ivanovska, 2014; Palmer, 1990; Sinclair, 1990). To be specific, Imre pointed out that modal verb express a variety of meanings, such as "possibility, necessity, politeness, etc" (p. 126). Furthermore, Ivanovska added that modal verbs convey the meanings as "probability, permission, volition and obligation" (p. 1093). For instance, the modal verb can in It can be good indicated the speaker's attitude of agreement.
In addition, it is noted that modal verbs could produce a particular effect, such as giving an instruction or making a request . For example, can in You can park the car here functions as an instruction. Modal verbs are types of auxiliary verbs which express necessity, ability, permission or possibility.
The most common modal verbs are can, may and must. Modal verbs don't have a past form and a past participle . When you use other tenses you have to replace them. Modal verbs are so common that most English speakers don't even know what the grammatical name for them is. Note that modal auxiliary verbs are a type of auxiliary verb. Auxiliary verbs encompass tenses, aspects, modality , voice, emphasis and so on.
There are many other category of verbs in English like phrasal verbs. In this ESL skills course you can learn natural English phrases. Learn even more about English grammar in this introduction to grammar course. These auxiliaries express obligation, possibilities, permission or ability in a sentence by adding meaning to the main verb. As per modal verbs rules, the spelling or form do not change, unlike other verbs. Modals/ modal verbs/ modal auxiliary verbs are a special type of verbs present in English grammar.
These verbs are used irregularly in English grammar. Uses of modal verbs in English grammar includes providing extra information about the action of the main verb. Modal verbs or modal auxiliary verbs are a type of verbs that indicates modality, i.e., likelihood, permission, ability and obligation. Some of the common modal verbs are can, could, may, might and must. Batstone defined this approach as a process of teaching which refers to the approach that engages learners in language use. In other words, teaching grammar should not only introduce the forms but also teach how to use accurately, meaningfully, and appropriately in different context.
This approach aims at concentrating learners' attention on meanings in context. As Thornbury sated, "if learners are going to be able to make sense of grammar, they will need to be exposed to it in its contexts of use" (p. 72). Thornbury put forward that "rules of use heavily depend on contextual factors" (p. 12).
For example, Sue can come could be understood differently in different contexts. In this example, the underlying meaning of can is possibility. However, when interpreting can from the speaker's view, it indicates that the speaker allows Sue to come, which is a kind of permission.
Meanwhile, from the listener's view, it can be comprehended as Sue is free on the day or Sue's leg is better, and she is able to walk again. As Lewis concludes, "the modal verbs always express the speaker's (or listener's) judgment or opinion at the moment of speaking". In this respect, in order to better understand the meaning of modal verbs, learners should take the specific context into consideration. In English, modal verbsare a small class of auxiliary verbs used to express ability, permission, obligation, prohibition, probability, possibility, advice. In the strict sense, though, these other verbs do not qualify as modal verbs in English because they do not allow subject-auxiliary inversion, nor do they allow negation with not.
If, however, one defines modal verb entirely in terms of meaning contribution, then these other verbs would also be modals and so the list here would have to be greatly expanded. This article mainly investigates on aspect of English grammar, modal verbs, which can be problematic for EFL learners in the Chinese teaching context. The difficulties in language learning and teaching, and rationales why modal verbs are tough to learn are examined. Then the two teaching approaches are examined, teaching the grammar works and contexts of use, which should be focused differently according to learners' level of proficiency.
The research on varying the relative complexity of teaching forms or language use needs to be further discussed in the future research. In Chinese grammar, the negative word is put before the modal verbs. Reliance on prior L1 knowledge, learners might put "not" in front of "could" and the sentence above could be incorrectly structured as He not could be over fifty. This indicates that L1 could interfere with L2 learning. As Ellis , and Larsen-Freeman and Long noted that the learner's L1 affects the other language levels. In the examples above, the form of the verb fall changes according to the rule of subject-verb agreement.
When the subject of the sentence is "I", "You", "We" or "They", the verb is fall. It can be seen from the second sentence that the form of the verb fall changes into falls when the subject is "He", "She" or "It". In EFL class, whereas, learners might tend to plus "-s" behind modal verbs when they find the subject in the sentence is the third person singular , such as he cans.
This problem is partly due to the learners' previous knowledge of grammar which follows the rule of the verb must agree in number with the subject. The grammatical form that can function as the modal in English grammar is the verb phrase. The nine auxiliary verbs, or modal verbs, that can function as the modal are the verbs can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, and would.
The five quasi-modal verbs that function as modals are ought , had better , used to, dare, and need. The modal verbs in English grammar are can, could, may, might, must, need not, shall/will, should/ought to. They express things like ability, permission, possibility, obligation etc.
They do not take -s in the simple present and they do not have a past simple or past participle form. However, some modal verbs have alternative forms that allow us to express the same ideas in different tenses. In many Germanic languages, the modal verbs may be used in more functions than in English. In German, for instance, modals can occur as non-finite verbs, which means they can be subordinate to other verbs in verb catenae; they need not appear as the clause root.
What Is Be Verb In English Grammar In Swedish, some modal verbs have infinitive forms. This for instance enables catenae containing several modal auxiliaries. The modal verbs are underlined in the following table.
As if English wasn't hard enough to learn, modal verbs complicate things even further. There are a lot of irregularities in the English language that can be confusing to students learning it as a second to their native tongue. English and other Germanic languages, however, utilize modal verbs to help express a function and are vital to gaining command of the English language.
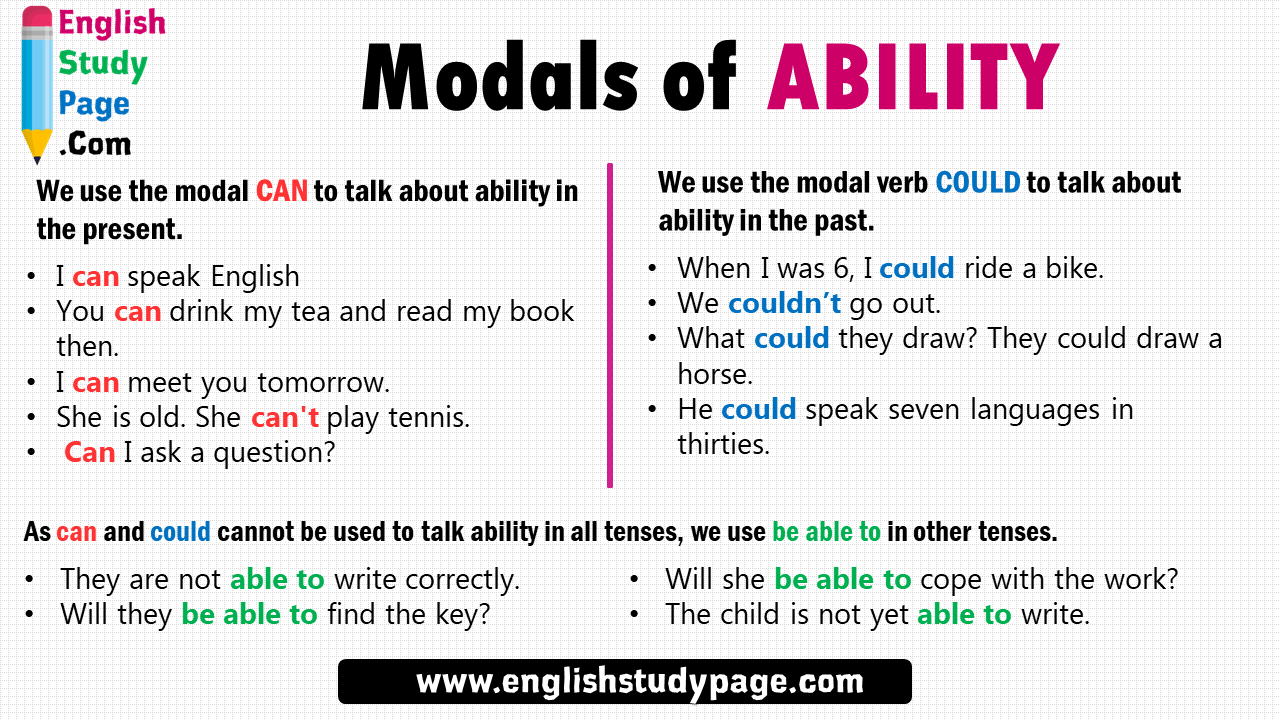
Abdul-Majeed and Hassoon pointed out that EFL learners are faced with serious problems in using modal verbs. Particularly, using modals properly is rather difficult for non-native speakers of English (Sedigheh, Marziyeh, & Jenaabadi, 2017). In English, the modal verbs are used to express ability, possibility, permission or obligation. Each one of the modal verbs can be used to express one or more of these modalities.
They can also be used to form the future tense in English and to make conditional sentences. Hawaiian Pidgin is a creole language most of whose vocabulary, but not grammar, is drawn from English. As is generally the case with creole languages, it is an isolating language and modality is typically indicated by the use of invariant pre-verbal auxiliaries. The invariance of the modal auxiliaries to person, number, and tense makes them analogous to modal auxiliaries in English.
However, as in most creoles the main verbs are also invariant; the auxiliaries are distinguished by their use in combination with a main verb. This podcast will use lots of examples to explain how 3 simple rules will help you use the most common modal verbs correctly. It tells you more - it tells you he has an obligation to go, he should go to school. Again no modal verb 'I sing a song', but with a modal verb 'I could sing a song'. I'm showing you it's a possibility - it may or may not happen, my song. So modal verbs are a way of showing a person's relationship with the verb.
So first of all, just in case you don't know - or you may not know the name - what are modal verbs in English? Well, they're words like 'could', 'can', 'should', 'may', 'might', 'ought', 'would', 'must'. And we use them with another verb - 'I could sing a song', 'You can travel abroad', 'He should go to school', 'She may support that charity'.
So we use these little modal verbs to give more information about the person's relationship with the action, with the main verb. Today we fix any mistakes you might make with English modal verbs. With just 3 simple rules, you will eliminate the main issues you can think of when using these tricky verbs.
If you have been having problems with learning English modal verb grammar , you must listen to this podcast. Since modal verbs are not the main verb in a sentence, they are not conjugated or inflected to show grammatical changes in the subject. The main use of the modal verb "will" is to form the future form of the verbs in English. When talking about demands and requests, the use of will sometimes is not as polite as other modal verbs.
The modal verb "might" is used to express possibility in the present or in the future. It can be used as the verb "may" most times, however, it often means that the event has less possibility of happening than when it's said using may. Its negative form, "might not " is used to talk about possibilities but in a negative way. It can be used to talk about ability and permission in the past. Also, just like the modal verb "can", the modal verb "could" can be used to make questions, requests, suggestions or offers, but in a more polite way.
It can also be used to talk about possibilities, but not as strong possibility that the one expressed with "can". There are a wide variety of modal auxiliary and their function. So, let's waste no more time and begin the learning journey. These modal verbs help you every day in your conversation.
To improve your English communication skills, you can join a course and learn grammar in-depth. A spoken English course will not only help you develop your English communication skills but also will make you fluent in the language. There are certain rules which surround the use of modal verbs, for example the word 'to' must never be used after a modal verb.
Learning these rules and how a modal verb can function within a sentence can greatly help you in forming grammatically correct sentences. Modals function within verb phrases functioning as predicates. Only one grammatical form can perform the function of modal in English. The one grammatical form that can function as the modal is the verb. Only the modal verbs can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, and would and the quasi-modal verbs ought , had better , used to, dare, and need can function as a modal. We use modal verbs to express ability, to give advice, to ask for and give permission, to express obligation, to express possibility, to deduce and to make predicitions.
Modal verbs are used to express ability, obligation, permission, assumptions, probability and possibility, requests and offers, and advice. Each modal verb can have more than one meaning which depends on the context of that sentence . Modal verbs, sometimes called modals, are auxiliary verbs .
They express such things as possibility, probability, permission and obligation. Modal verbs are auxiliary verbs that express a speaker's attitude and the strength of that attitude. They have multiple meanings and sometimes overlap in ways that are confusing to English learners. Remember Rule Number Three - for negative modal verbs, just a simple 'not' between the modal and the main verb - I can not drive a car. This one contracts two ways 'I cannot drive a car' or 'I can't drive a car'.
Let's pretend that you're the English teacher and you have some sentences to correct, where the modal verbs have been used wrongly, used incorrectly. Being the teacher and correcting mistakes is sometimes a good way to check that you know how to do it well. And think about which of the three easy rules for modal verbs is being broken in each of these sentences.
And do you have problems with modal verbs in English? If you do, you'll know that modal verbs appear all the time in English. So if you want to speak English without mistakes, you have to learn modal verbs.